Credential Stuffing Explained in Plain English for Non-Tech People
The Internet
What is a Browser
What is Cache
What is a Cookie
What is Data in Transit
What is Data at Rest
What is a Data Packet
What is DNS
What is Encryption
What is End-to-End Encryption
What is HTTP/HTTPS
What is SSL/TLS
Your Company Network
What is Antivirus Software
What is DNS Content Filtering
What is Advanced Endpoint Security
What is a Firewall
What is a Modem
What is a Network
What is Remote Desktop (RDP)
Work from Anywhere
What is a Home Network
What is a Hotspot
What is a VPN
What is Wi-Fi
Life in the Cloud
What is the Cloud
Your Company Assets
What is Access Rights
What is a Data Inventory
What is Shadow IT
What is a Software Inventory
What is a Technology Roadmap
What is IT Asset Management (ITAM)
What are User Access Rights
Your Security Essentials
What is a Brute Force Attack
What is Credential Stuffing
What is an IP Blacklist
What is a Keylogger
What is Malware
What is Warshipping
What is a Whitelist
What is a Browser
What is Cache
What is a Cookie
What is Data in Transit
What is Data at Rest
What is a Data Packet
What is DNS
What is Encryption
What is End-to-End Encryption
What is HTTP/HTTPS
What is SSL/TLS
Your Company Network
What is Antivirus Software
What is DNS Content Filtering
What is Advanced Endpoint Security
What is a Firewall
What is a Modem
What is a Network
What is Remote Desktop (RDP)
Work from Anywhere
What is a Home Network
What is a Hotspot
What is a VPN
What is Wi-Fi
Life in the Cloud
What is the Cloud
Your Company Assets
What is Access Rights
What is a Data Inventory
What is Shadow IT
What is a Software Inventory
What is a Technology Roadmap
What is IT Asset Management (ITAM)
What are User Access Rights
Your Security Essentials
What is a Brute Force Attack
What is Credential Stuffing
What is an IP Blacklist
What is a Keylogger
What is Malware
What is Warshipping
What is a Whitelist
What is Credential Stuffing?
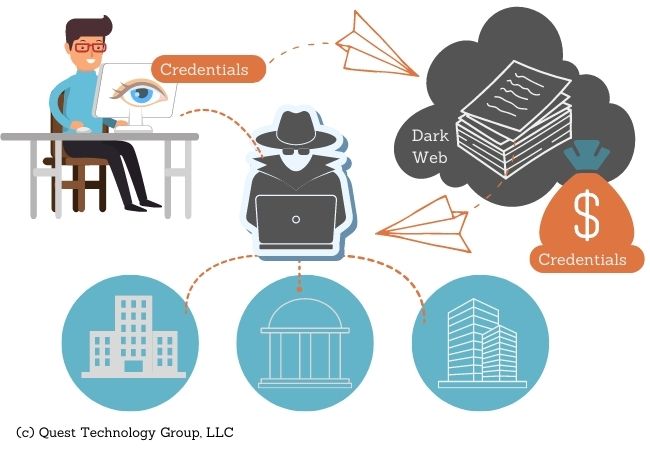
Credential stuffing is a cyber attack where login credentials stolen through one organization's data breach are used to access another unrelated organization, site or service.
For example, suppose your manufacturing company, We Make Amazing Stuff, has a data breach and your employees’ user login information is taken in the heist. Attackers use these stolen login credentials to attempt access to your employees’ bank or healthcare provider services.
Neither the bank nor the healthcare company were involved in this (or maybe any) data breach. They simply became unsuspecting players in this attack chain.
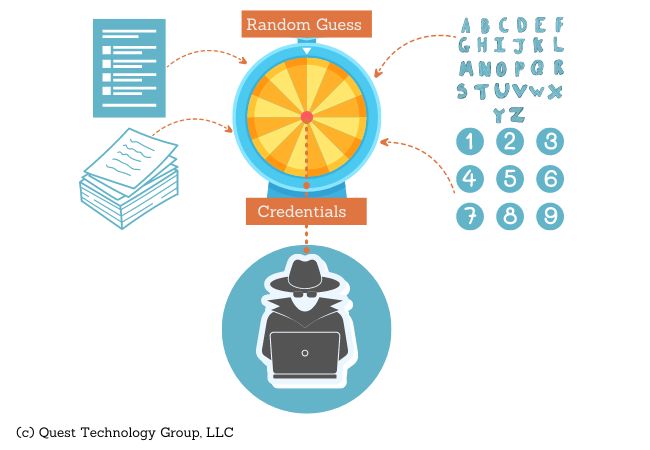
Attackers know that a lot of us use the same username and password for more than one account. In many cases, our username is our email address which is even easier to obtain. 50% of the work has already been done for the attacker.
It's easy work for an attacker to try these same credentials with other companies, knowing they will likely have a small percentage of successful hits.
Why is Credential Stuffing Effective?
6 Ways to Help Prevent Credential Stuffing
It's important to know that MFA doesn't ensure that credentials can't be compromised. Hackers are continually finding new ways to circumvent safeguards. Documented cases are published in the security community regularly.
Leading technology companies, such as Microsoft, Apple, and Google, know that bad actors are relentless in their thievery. These forward-thinking companies are rolling out the better-than-MFA level of user identify security.
Microsoft, for example, has implemented passwordless authentication in Azure that doesn't use the authentication codes and tokens you commonly receive for MFA.
If your company provides a client portal or application that requires user login, implementing MFA is a smart security practice.
How to Check Your Passwords
If you’re curious about the integrity of your passwords, this is an easy checkup.
This free web resource was created in 2017 in response to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) password management guidance. Your passwords will be checked against a database of hundreds of millions of passwords involved in data breaches.
https://haveibeenpwned.com/Passwords
Keep Discovering
What is a Keylogger
What is Malware
What is Warshipping

