Understand the baffling technology words and phrases you hear every day.
The Internet
What is a Browser
What is Cache
What is a Cookie
What is Data in Transit
What is Data at Rest
What is a Data Packet
What is DNS
What is Encryption
What is End-to-End Encryption
What is HTTP/HTTPS
What is SSL/TLS
Your Company Network
What is Antivirus Software
What is DNS Content Filtering
What is Advanced Endpoint Security
What is a Firewall
What is a Modem
What is a Network
What is Remote Desktop (RDP)
Work from Anywhere
What is a Home Network
What is a Hotspot
What is a VPN
What is Wi-Fi
Life in the Cloud
What is the Cloud
Your Company Assets
What is Access Rights
What is a Data Inventory
What is Shadow IT
What is a Software Inventory
What is a Technology Roadmap
What is IT Asset Management (ITAM)
What are User Access Rights
Your Security Essentials
What is a Brute Force Attack
What is Credential Stuffing
What is an IP Blacklist
What is a Keylogger
What is Malware
What is Warshipping
What is a Whitelist
What is a Browser
What is Cache
What is a Cookie
What is Data in Transit
What is Data at Rest
What is a Data Packet
What is DNS
What is Encryption
What is End-to-End Encryption
What is HTTP/HTTPS
What is SSL/TLS
Your Company Network
What is Antivirus Software
What is DNS Content Filtering
What is Advanced Endpoint Security
What is a Firewall
What is a Modem
What is a Network
What is Remote Desktop (RDP)
Work from Anywhere
What is a Home Network
What is a Hotspot
What is a VPN
What is Wi-Fi
Life in the Cloud
What is the Cloud
Your Company Assets
What is Access Rights
What is a Data Inventory
What is Shadow IT
What is a Software Inventory
What is a Technology Roadmap
What is IT Asset Management (ITAM)
What are User Access Rights
Your Security Essentials
What is a Brute Force Attack
What is Credential Stuffing
What is an IP Blacklist
What is a Keylogger
What is Malware
What is Warshipping
What is a Whitelist
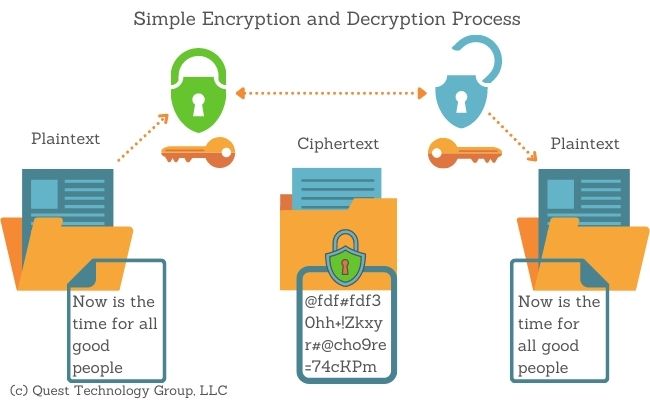
What is Encryption?
Encryption is the method of changing plaintext that humans can read into human-unreadable scrambled letters, numbers, and symbols. Encrypting and decrypting data is called cryptography.
Think of plaintext as an open window. Anyone can look in and see what is in the room. Encrypting the text is like closing the blinds. Only someone with access to the cord can open the blinds.
Opening the blinds is decrypting the data.

Why is Encryption Important?
Encryption protects information so only people who should have access to it can do so. It is used both for data stored on computers and storage devices and for sending data across networks. The networks can be an internal company network, a home network, or the internet.
How Does Encryption Work?
Encryption uses an algorithm called a cipher to convert plaintext into scrambled characters known as ciphertext. This complex algorithm generates a key that only an authorized person can use to decrypt the data.
There are several different algorithms available to perform encyrption. We'll save that explanation for a deeper dive.
As you explore encryption more, you will hear the phrases private keys and public keys. They both lock and unlock data but in different ways. To keep this simple, a key in this illustration can be either public or private.
Keep Learning
What is End-to-End Encryption?
What is Data at Rest?
