Understand the baffling technology words and phrases you hear every day.
The Internet
What is a Browser
What is Cache
What is a Cookie
What is Data in Transit
What is Data at Rest
What is a Data Packet
What is DNS
What is Encryption
What is End-to-End Encryption
What is HTTP/HTTPS
What is SSL/TLS
Your Company Network
What is Antivirus Software
What is DNS Content Filtering
What is Advanced Endpoint Security
What is a Firewall
What is a Modem
What is a Network
What is Remote Desktop (RDP)
Work from Anywhere
What is a Home Network
What is a Hotspot
What is a VPN
What is Wi-Fi
Life in the Cloud
What is the Cloud
Your Company Assets
What is Access Rights
What is a Data Inventory
What is Shadow IT
What is a Software Inventory
What is a Technology Roadmap
What is IT Asset Management (ITAM)
What are User Access Rights
Your Security Essentials
What is a Brute Force Attack
What is Credential Stuffing
What is an IP Blacklist
What is a Keylogger
What is Malware
What is Warshipping
What is a Whitelist
What is a Browser
What is Cache
What is a Cookie
What is Data in Transit
What is Data at Rest
What is a Data Packet
What is DNS
What is Encryption
What is End-to-End Encryption
What is HTTP/HTTPS
What is SSL/TLS
Your Company Network
What is Antivirus Software
What is DNS Content Filtering
What is Advanced Endpoint Security
What is a Firewall
What is a Modem
What is a Network
What is Remote Desktop (RDP)
Work from Anywhere
What is a Home Network
What is a Hotspot
What is a VPN
What is Wi-Fi
Life in the Cloud
What is the Cloud
Your Company Assets
What is Access Rights
What is a Data Inventory
What is Shadow IT
What is a Software Inventory
What is a Technology Roadmap
What is IT Asset Management (ITAM)
What are User Access Rights
Your Security Essentials
What is a Brute Force Attack
What is Credential Stuffing
What is an IP Blacklist
What is a Keylogger
What is Malware
What is Warshipping
What is a Whitelist
What is HTTP?
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is the method used to connect to web servers on the internet or on a local network, called an intranet. This connection sends web pages from the server to the user's browser. It can also send and download data from the web server to the user's browser or an application.
How Does HTTP Work?
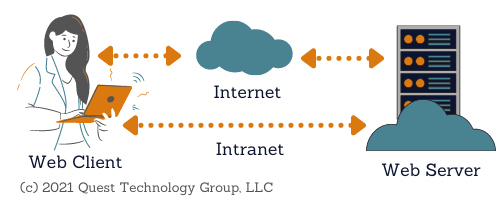
When you enter a website name (URL) in your browser or click a website link, your browser immediately sends a request to a web server. Your request travels over the internet or local network to find and deliver the website to you.
How is HTTPS Different Than HTTP?

HTTPS is the secure version of HTTP. When a connection is requested, the session is managed by a security protocol such as TLS. This security layer creates end-to-end encryption for the entire request.
HTTPS is the protocol that should be implemented on all websites today. Without this level of encryption, data passing between your website request and the web pages returned to your browser is easily intercepted by hackers. Always look for the green lock and https:// when you arrive at a website. If the website isn't secure, then do not continue.
What is a Protocol in Technology?
A protocol is an established set of rules that are followed for specific procedures or tasks. For example, a security protocol's job is to ensure that data is transmitted across networks protected against unauthorized users' access.
Keep Learning
How Do You Get to a Website? (PDF)
What is DNS?
What is End-to-End Encryption?
What is SSL/TLS?
. . . . .
